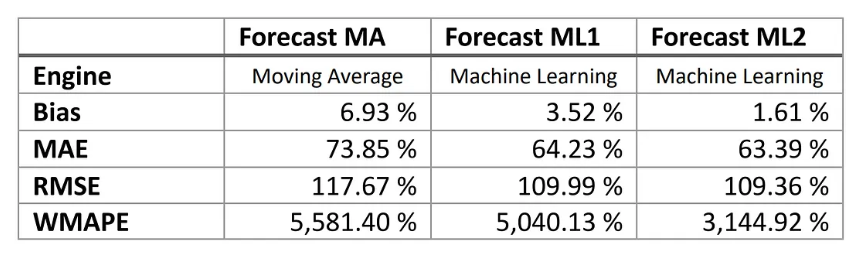
Forecasting plays a critical role in every business’s success. Whether you’re planning inventory, setting revenue goals, or projecting customer demand, accurate forecasts can help you make smarter decisions, reduce risk, and seize new opportunities. But getting it right isn’t always easy.
In this guide, we’ll break down the strategies, tools, and best practices that can help improve your forecasting efforts. By the end, you’ll have actionable insights to refine your predictions and grow with confidence.
Contents
- 1 What Is Forecasting in Business?
- 2 Why Accuracy Matters in Forecasting
- 3 Common Forecasting Challenges
- 4 1. Start with Clean, Reliable Data
- 5 2. Choose the Right Method
- 6 3. Leverage Modern Technology
- 7 4. Segment Your Data
- 8 5. Set Clear Objectives
- 9 6. Incorporate External Variables
- 10 7. Monitor Results Regularly
- 11 8. Train and Educate Your Team
- 12 9. Collaborate Across Departments
- 13 10. Update Frequently
- 14 11. Test Scenarios
- 15 12. Use Results to Drive Strategy
- 16 13. Learn from Mistakes
- 17 Conclusion: Make Forecasting a Competitive Advantage
- 18 FAQs
What Is Forecasting in Business?

Forecasting is the process of using historical data, market trends, and analytics to predict future outcomes. Businesses use it for a variety of purposes, including:
- Sales projections
- Financial planning
- Demand analysis
- Cash flow management
- Inventory planning
- Workforce scheduling
By anticipating what may happen next through well-informed estimates, businesses can allocate resources effectively, avoid unnecessary costs, and stay competitive.
Why Accuracy Matters in Forecasting
Precise projections help businesses:
- Improve decision-making: Make informed choices about operations, marketing, and budgeting.
- Optimize resources: Avoid overstocking or understocking inventory.
- Increase profitability: Reduce waste, improve efficiency, and align pricing strategies.
- Mitigate risks: Prepare for economic downturns, demand fluctuations, or supply chain issues.
Inaccurate predictions, on the other hand, can lead to poor planning, missed sales targets, and financial instability.
Common Forecasting Challenges
Before improving forecasting accuracy, it’s important to recognize the obstacles many businesses face:
- Lack of historical data
- Poor data quality
- Failure to update projections regularly
- Unrealistic assumptions
- Limited use of advanced tools
If your business struggles with any of these, you’re not alone. The good news? There are practical strategies to overcome them.
1. Start with Clean, Reliable Data
Your estimates are only as good as the data they’re built on. Garbage in, garbage out. Here’s how to ensure your information is dependable:
- Clean your data: Remove duplicates, fix inconsistencies, and update missing values.
- Centralize your data sources: Use integrated systems (like CRMs and ERPs) to reduce data silos.
- Validate accuracy: Cross-check against reliable sources and historical benchmarks.
Investing in data hygiene might take time initially, but it pays off in more dependable outcomes.
2. Choose the Right Method
Different situations require different approaches. Here are some commonly used forecasting techniques:
Qualitative Methods
- Based on expert opinions, market research, and surveys.
- Best when you lack historical data (e.g., for new product launches).
Quantitative Models
- Uses historical data and statistical formulas.
- Best for established businesses with reliable records.
Time Series Techniques
- Projects future data points based on past trends (e.g., seasonal sales).
Causal Analysis
- Analyzes relationships between variables (e.g., advertising spend vs. sales growth).
Use a combination of methods if needed. Hybrid models often yield more accurate results.
3. Leverage Modern Technology
Software can automate calculations and deliver more precise predictions. Consider these tools:
- Microsoft Excel with add-ins
- Google Sheets with predictive functions
- Advanced platforms like Tableau, Power BI, or SAS
- AI-based tools like Fivetran, DataRobot, or Forecast Pro
These platforms use algorithms and machine learning to analyze patterns and improve accuracy by spotting anomalies you might miss manually.
4. Segment Your Data
Not all data should be treated equally. Segmenting your information improves clarity and precision.
Examples:
- Customer types (e.g., new vs. repeat buyers)
- Product categories (e.g., fast-moving vs. slow-moving inventory)
- Geographic locations
This lets you make more precise predictions and identify which areas drive your business performance.
5. Set Clear Objectives
Without defined targets, your efforts can lose focus. Here’s how to set smart goals:
- Be specific: Estimate revenue for Q4 2025, not just “next quarter.”
- Set a time frame: Weekly, monthly, quarterly.
- Align with strategy: Match your projections to marketing campaigns, product launches, or expansion plans.
Clear goals help your team understand what’s being measured—and why.
6. Incorporate External Variables
Relying only on internal data isn’t enough. Consider outside factors such as:
- Market trends
- Economic indicators
- Competitor activity
- Weather or seasonality
- Regulatory changes
These can significantly impact your business outlook, especially in industries like retail, travel, or agriculture.
7. Monitor Results Regularly
Projections shouldn’t be “set and forget.” Track how they perform against real outcomes:
- Use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error)
- Identify recurring gaps or patterns
- Adjust models based on actual performance
Regular monitoring allows for continuous improvement.
8. Train and Educate Your Team
Your projections are only as strong as the people behind them. Invest in training for:
- Data analysis skills
- Methodology selection
- Tool proficiency (e.g., Excel, BI dashboards)
A knowledgeable team ensures your process stays relevant and reliable.
9. Collaborate Across Departments
Sales, finance, marketing, and operations should all have a seat at the planning table. Why?
- Sales knows customer demand.
- Marketing understands campaigns that will influence demand.
- Finance aligns efforts with budgets.
- Operations ensures capacity planning.
Collaboration avoids blind spots and fosters company-wide buy-in.
10. Update Frequently
Business environments change rapidly. Your projections should keep pace:
- Schedule regular updates (monthly, weekly, or real-time)
- Use rolling forecasts instead of static, annual ones
- Adjust based on new data, market changes, or business shifts
Frequent updates lead to more responsive and accurate results.
11. Test Scenarios
Scenario planning helps you prepare for multiple outcomes. Example scenarios:
- Best-case, worst-case, and most-likely
- Sales spikes due to promotions
- Supply chain disruptions
Testing your assumptions under different conditions highlights strengths, weaknesses, and risks.
12. Use Results to Drive Strategy
These insights should influence more than just operations. Use your analysis to:
- Launch new products
- Expand into new markets
- Hire and allocate workforce resources
- Adjust pricing and promotional strategies
Strategic application of your findings allows you to lead rather than react.
13. Learn from Mistakes
Review past efforts and identify what went wrong:
- Were the assumptions incorrect?
- Was the data incomplete?
- Did external events disrupt expectations?
Analyzing past errors improves future efforts and builds resilience.
Conclusion: Make Forecasting a Competitive Advantage
Forecasting isn’t just a numbers game—it’s a strategic tool that can make or break your business. By focusing on data quality, using the right tools, involving your team, and continuously refining your approach, you can achieve much better results.
FAQs
Q: What is the most accurate method of forecasting?
A: It depends on your business type and data availability. Time-series and machine learning models often offer high accuracy when properly implemented.
Q: How often should I update my forecasting estimates?
A: Ideally, projections should be updated monthly or in real-time, depending on your business pace.
Q: What industries benefit most from forecasting?
A: All industries can benefit, especially retail, manufacturing, finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Q: Can small businesses use forecasting too?
A: Absolutely! Even basic models can help small businesses make better decisions and manage resources effectively.
Q: Is AI necessary for accurate forecasting?
A: Not necessary, but AI can significantly enhance precision, especially for businesses dealing with large, complex datasets.