In today’s fast-paced digital world, the need for strong cybersecurity measures has never been more important. With businesses relying more heavily on remote work, cloud-based applications, and mobile devices, the security perimeter has dramatically expanded. One of the most effective ways to protect this perimeter is through endpoint software security. But why is endpoint software security critical? This guide will break down its importance, how it works, and why every organization large or small should prioritize it.
Contents
- 1 What Is Endpoint Software Security?
- 2 The Rising Threat Landscape
- 3 Why Endpoint Software Security Is Critical
- 4 Key Features of Effective Endpoint Software Security
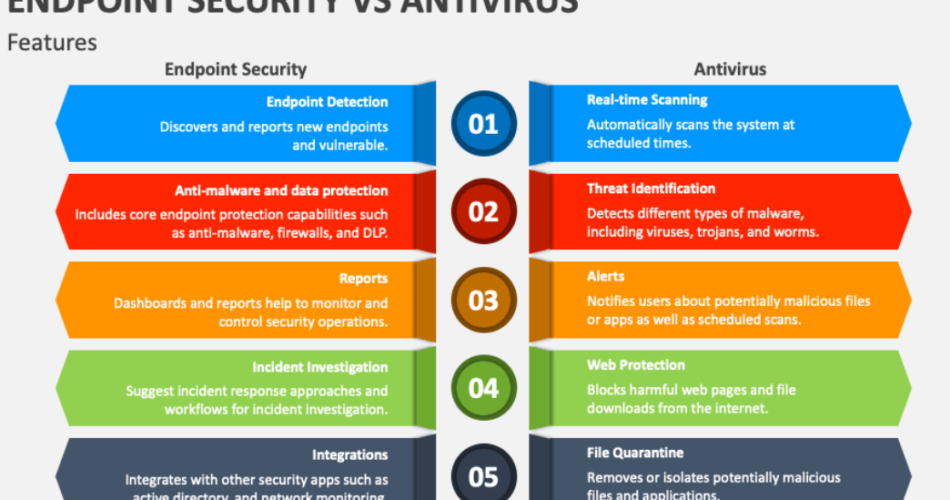
- 5 Endpoint Security vs. Traditional Antivirus Software
- 6 Real-World Scenarios
- 7 How to Implement Endpoint Software Security
- 8 Common Challenges in Endpoint Software Security
- 9 Future of Endpoint Software Security
- 10 Conclusion
What Is Endpoint Software Security?

Endpoint software security refers to the protection of internet-connected devices such as laptops, desktops, mobile phones, tablets, and servers. These devices—referred to as endpoints—serve as points of access to an enterprise network. If not properly secured, endpoints become prime targets for cybercriminals looking to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive data, or deploy malicious software.
Endpoint software security uses specialized applications and tools designed to detect, prevent, and respond to threats that target these endpoints.
The Rising Threat Landscape
Cyberattacks are not just increasing in frequency—they are becoming more sophisticated. The rise in remote work and the proliferation of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies have added more complexity to cybersecurity. According to recent studies:
- More than 70% of successful breaches originate at the endpoint.
- Ransomware attacks increased by over 150% in the last year.
- Phishing attacks remain the most common method of initiating endpoint breaches.
This evolving threat landscape makes endpoint software security an absolute necessity.
Why Endpoint Software Security Is Critical
Let’s explore the key reasons why endpoint software security should be a central component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
1. Multiple Devices, Multiple Entry Points
Every device that connects to your network increases the potential for a breach. With employees using multiple devices for work—including smartphones, tablets, and personal laptops—each one becomes a new access point. Endpoint software security ensures that all these devices are monitored and protected.
2. Protection Against Malware and Ransomware
Cybercriminals frequently use malware and ransomware to exploit vulnerable endpoints. Endpoint software security tools can detect these threats in real-time and isolate affected devices to prevent the spread of malicious software across the network.
3. Data Loss Prevention
Data breaches can lead to severe financial and reputational damage. Endpoint software security includes data loss prevention features that monitor data transfers and flag any suspicious activity. This is especially important for industries like healthcare and finance that deal with sensitive personal data.
4. Centralized Management
One of the greatest benefits of modern endpoint software security solutions is the ability to manage all endpoints from a centralized console. This allows IT administrators to enforce policies, monitor activity, and respond to threats quickly and efficiently.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal services must comply with strict data protection laws like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. Endpoint software security helps meet these requirements by ensuring that endpoints meet the necessary security standards.
6. Supports Remote and Hybrid Work
With remote work becoming the norm, employees often work from unsecured networks. Endpoint software security helps bridge this gap by providing secure access, even from remote or unknown locations.
7. Cost-Effective Risk Mitigation
While investing in endpoint security may seem costly upfront, it is far more economical than dealing with the aftermath of a cyberattack. Data recovery, legal fees, and loss of customer trust can far exceed the cost of a robust security solution.
Key Features of Effective Endpoint Software Security
A powerful endpoint software security solution should include the following features:
- Antivirus and Antimalware Protection
- Firewall Integration
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention
- Data Encryption
- Patch Management
- Device Control and Application Whitelisting
- Behavioral Analysis and AI-driven Threat Detection
- Cloud-based Management Console
Endpoint Security vs. Traditional Antivirus Software
Many people assume antivirus software is enough to protect their devices. However, traditional antivirus solutions often fail to address modern, complex threats. Here’s how endpoint software security stands apart:
| Feature | Antivirus Software | Endpoint Software Security |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Monitoring | Limited | Advanced, AI-driven |
| Multi-Device Protection | Usually Single Device | Enterprise-Wide Coverage |
| Threat Intelligence | Basic Signatures | Behavioral + Predictive Analysis |
| Central Management | No | Yes |
| Data Encryption | Rare | Common |
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Remote Employee Phishing Attack
An employee working from home clicks on a phishing link disguised as a work-related email. Traditional antivirus may not flag it. However, endpoint software security detects the suspicious behavior, isolates the device, and prevents further damage.
Scenario 2: Insider Threat
An employee tries to transfer sensitive files to an unauthorized external drive. Endpoint software security flags this as suspicious and blocks the action, alerting the IT team in real-time.
How to Implement Endpoint Software Security
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
Understand the number and types of endpoints in your organization. Consider devices, user roles, and the level of access needed.
Step 2: Choose the Right Solution
Look for a solution that fits your organization’s size and complexity. Popular endpoint software security providers include:
- Symantec
- Bitdefender
- CrowdStrike
- McAfee
- Sophos
- SentinelOne
Step 3: Develop Policies
Create usage policies for devices, especially for BYOD scenarios. Clearly define what is allowed and what isn’t.
Step 4: Train Employees
The human element is often the weakest link. Train your team to recognize phishing attempts, use secure passwords, and follow best practices.
Step 5: Monitor and Update Regularly
Endpoint security is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution. Regular updates and monitoring are crucial to adapt to evolving threats.
Common Challenges in Endpoint Software Security
- Device Proliferation: Managing a growing number of devices can be difficult.
- BYOD Policies: Personal devices may not meet company security standards.
- User Negligence: Employees may unknowingly bypass security protocols.
- Sophisticated Threats: New, intelligent malware can bypass traditional detection methods.
To mitigate these issues, businesses must stay vigilant and proactive.
Future of Endpoint Software Security
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must endpoint software security. Future trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning for predictive threat detection.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Never trust, always verify.
- Cloud-Native Endpoint Protection for scalability.
- Integration with XDR (Extended Detection and Response) for a holistic approach to security.
Conclusion
Endpoint software is not just a luxury it’s a necessity in our digital age. With cyber threats on the rise, organizations must take proactive steps to protect every device that connects to their network. From preventing data breaches to ensuring regulatory compliance, endpoint software security is a cornerstone of a strong cybersecurity strategy.