Financial statement preparation is a crucial process for businesses, organizations, and individuals. Accurate financial statements provide a clear picture of financial health, guide decision-making, and ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Whether you’re a business owner, an accountant, or a finance professional, understanding the fundamentals of financial statement preparation is essential.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about preparing financial statements, including their components, the process, key principles, and best practices to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Contents
- 1 What is Financial Statement Preparation?
- 2 The Key Components of Financial Statements
- 3 The Financial Statement Preparation Process
- 4 Key Accounting Principles for Financial Statement Preparation
- 5 Best Practices for Financial Statement Preparation
- 6 Common Challenges in Financial Statement Preparation
- 7 Why Financial Statement Preparation is Important
- 8 Conclusion
What is Financial Statement Preparation?

Financial statement preparation refers to the process of compiling financial data into structured reports that summarize a company’s financial activities. These statements provide a snapshot of financial performance and position over a specific period, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
Companies, investors, banks, and regulators rely on financial statements to assess profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. Proper financial statement preparation ensures transparency and trust in financial reporting.
The Key Components of Financial Statements
There are three main financial statements that businesses prepare:
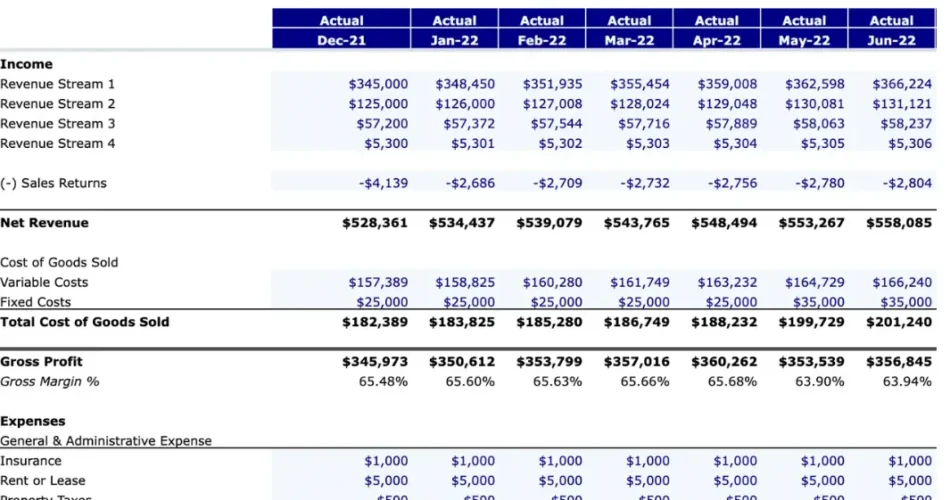
1. Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
The income statement shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. It helps assess profitability and operational efficiency.
Key Elements:
- Revenue (Sales)
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
- Gross Profit
- Operating Expenses
- Net Income (or Loss)
2. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given date, showing assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
Key Elements:
- Assets (Current and Non-Current)
- Liabilities (Current and Long-Term)
- Shareholders’ Equity
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash within the business, helping assess liquidity and cash management.
Key Sections:
- Operating Activities
- Investing Activities
- Financing Activities
The Financial Statement Preparation Process
To ensure accuracy and compliance, follow these steps when preparing financial statements:
Step 1: Gather Financial Data
Start by collecting all relevant financial data, including sales records, expense reports, payroll information, and bank statements.
Step 2: Record Transactions in the General Ledger
Ensure that all financial transactions are recorded in the general ledger using the appropriate accounting system.
Step 3: Adjust Entries
Make necessary adjustments for accrued expenses, depreciation, or prepaid expenses to ensure accurate reporting.
Step 4: Prepare a Trial Balance
A trial balance helps verify that debits and credits are balanced before creating the financial statements.
Step 5: Create Financial Statements
Using the verified data, prepare the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Step 6: Review and Finalize
Double-check all calculations, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and finalize the reports.
Key Accounting Principles for Financial Statement Preparation
To maintain accuracy and compliance, financial statements must adhere to established accounting principles, such as:
1. Accrual Accounting
Revenue and expenses should be recorded when they are incurred, not when cash is received or paid.
2. Consistency Principle
Accounting methods should be applied consistently across reporting periods to ensure comparability.
3. Going Concern Principle
Financial statements should assume that the business will continue operating in the foreseeable future.
4. Materiality Principle
Financial statements should include all information that could influence decision-making.
5. Full Disclosure Principle
All relevant financial information must be disclosed to provide a complete picture of the company’s financial position.
Best Practices for Financial Statement Preparation
To ensure accuracy and reliability, follow these best practices:
1. Use Accounting Software
Utilizing accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, or FreshBooks can streamline financial statement preparation and reduce errors.
2. Keep Detailed Records
Maintain organized and up-to-date financial records to simplify statement preparation and audits.
3. Reconcile Bank Statements Regularly
Frequent bank reconciliations help identify discrepancies and ensure accuracy.
4. Follow Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to accounting standards such as GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) or IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards).
5. Work with a Professional Accountant
If financial statements are complex, consulting an accountant ensures accuracy and compliance with regulations.
Common Challenges in Financial Statement Preparation
1. Inaccurate Data Entry
Errors in recording transactions can lead to misleading financial reports.
2. Misclassification of Accounts
Incorrectly categorizing expenses or revenues can distort financial statements.
3. Lack of Internal Controls
Weak internal controls can result in fraud or financial mismanagement.
4. Failure to Adjust Entries
Not accounting for accrued expenses, depreciation, or prepayments can affect financial accuracy.
5. Non-Compliance with Accounting Standards
Failing to follow accounting principles can lead to regulatory issues and penalties.
Why Financial Statement Preparation is Important
1. Decision Making
Business owners and managers rely on financial statements to make informed operational and strategic decisions.
2. Investor Confidence
Accurate and transparent financial statements attract investors and enhance credibility.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Regulatory bodies require financial statements for tax filings and audits.
4. Financial Planning and Budgeting
Financial statements provide valuable insights for future budgeting and financial planning.
5. Loan and Credit Applications
Lenders use financial statements to assess a company’s creditworthiness before approving loans.
Conclusion
Financial statement preparation is a fundamental aspect of financial management. By understanding the key components, following a structured process, and adhering to accounting principles, businesses can ensure accuracy, compliance, and reliability in their financial reporting.
Whether you’re a small business owner, a financial professional, or an investor, mastering financial statement preparation can help you make informed financial decisions and maintain financial stability. Utilizing best practices, staying updated with accounting standards, and leveraging technology will further streamline the process and improve financial transparency.