Contents
- 1 What is Tiered Link Building?
- 2 Why Use a Tiered Link Building Structure?
- 3 Advantages of Tiered Link Building
- 4 Disadvantages of Tiered Link Building
- 5 How to Implement a Tiered Link Building Structure
- 6 Best Practices for Tiered Link Building
- 7 Tools to Support Tiered Link Building
- 8 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 9 Conclusion
What is Tiered Link Building?
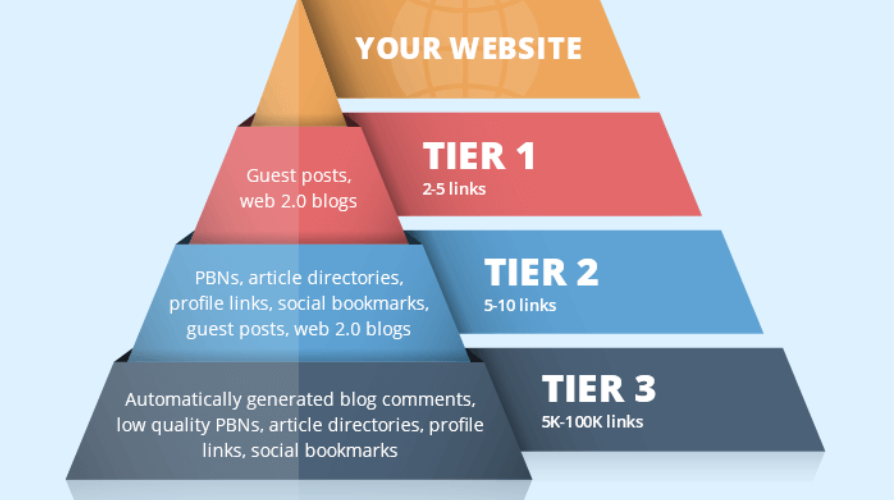
Tiered Link Building Structure
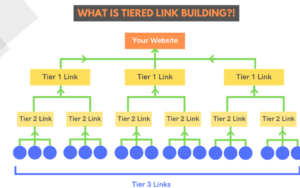
Tiered link building is a strategic approach to creating a multi-level backlink structure to improve your website’s authority and rankings. Instead of focusing solely on acquiring direct backlinks to your website (Tier 1), this method involves building additional layers of links (Tier 2, Tier 3, etc.) that point to your Tier 1 links. The goal is to create a cascading effect that strengthens the authority of your primary backlinks and, in turn, boosts your website’s SEO performance.
The Tiers Explained:
- Tier 1 Links: These are high-quality backlinks pointing directly to your website. They should come from authoritative, relevant, and trustworthy sources.
- Tier 2 Links: These links point to your Tier 1 links. They help boost the authority of your Tier 1 backlinks.
- Tier 3 Links: These links point to your Tier 2 links, creating a further layer of support for your backlink structure.
Why Use a Tiered Link Building Structure?
- Enhanced Link Authority: By building supporting links (Tier 2 and Tier 3), you strengthen the authority of your Tier 1 links, making them more valuable in the eyes of search engines.
- Improved Rankings: A well-structured tiered link-building strategy can lead to higher rankings for your target keywords.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversifying your backlink profile across multiple tiers reduces the risk of penalties from search engines, as it mimics natural link-building patterns.
- Scalability: Tiered link building allows you to scale your efforts by focusing on multiple layers of links rather than just direct backlinks.
Advantages of Tiered Link Building
- Increased Website Authority: By building a multi-tiered backlink structure, you enhance the authority of your Tier 1 links, which positively impacts your website’s overall domain authority.
- Improved Search Engine Rankings: Strengthening your Tier 1 links through Tier 2 and Tier 3 links can lead to higher rankings for your target keywords.
- Natural Link Profile: A tiered approach mimics natural link-building patterns, making your backlink profile appear more organic to search engines.
- Risk Diversification: By spreading your link-building efforts across multiple tiers, you reduce the risk of penalties from search engines.
- Cost-Effective: Tier 2 and Tier 3 links are often easier and cheaper to acquire than high-quality Tier 1 links, making this strategy cost-effective.
- Scalability: You can scale your efforts by focusing on multiple layers of links, allowing for more comprehensive SEO campaigns.
Disadvantages of Tiered Link Building
- Time-Consuming: Building and managing multiple tiers of links requires significant time and effort.
- Complexity: Managing a tiered link-building strategy can be complex, especially for beginners.
- Risk of Low-Quality Links: If not done carefully, Tier 2 and Tier 3 links can come from low-quality or spammy sources, which may harm your SEO efforts.
- Potential for Over-Optimization: Over-optimizing your anchor text or link structure can lead to penalties from search engines.
- Dependence on Tier 1 Links: If your Tier 1 links are not strong or relevant, the entire structure may fail to deliver the desired results.
- Algorithm Changes: Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving, and what works today may not work tomorrow, making it essential to stay updated.
How to Implement a Tiered Link Building Structure
Step 1: Build High-Quality Tier 1 Links
Your Tier 1 links are the foundation of your strategy. Focus on acquiring backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites. Here’s how:
- Guest Blogging: Write high-quality guest posts for reputable websites in your niche.
- Outreach Campaigns: Reach out to industry influencers, bloggers, and journalists for link placements.
- Content Marketing: Create shareable, link-worthy content like infographics, research studies, or in-depth guides.
- Directory Submissions: Submit your website to high-quality, niche-specific directories.
- Broken Link Building: Find broken links on authoritative websites and suggest your content as a replacement.
SEO Considerations for Tier 1 Links:
- Ensure the websites linking to you have high domain authority (DA) and trust flow (TF).
- Use relevant anchor text that aligns with your target keywords.
- Avoid spammy or low-quality websites to prevent penalties.
Step 2: Build Tier 2 Links to Support Tier 1
Tier 2 links are designed to boost the authority of your Tier 1 links. These can be slightly lower in quality but should still come from credible sources. Examples include:
- Web 2.0 Properties: Create content on platforms like Medium, WordPress.com, or Blogger, and link to your Tier 1 links.
- Social Bookmarks: Submit your Tier 1 links to social bookmarking sites like Reddit, Pinterest, or Mix.
- Forum Profiles: Participate in niche forums and include links to your Tier 1 content in your profile or discussions.
- Article Submissions: Publish articles on article directories like EzineArticles or HubPages, linking back to your Tier 1 links.
SEO Considerations for Tier 2 Links:
- Use a mix of branded and generic anchor text to maintain a natural link profile.
- Avoid over-optimization by varying your anchor text and link sources.
- Focus on platforms that are relevant to your niche.
Step 3: Build Tier 3 Links to Strengthen Tier 2
Tier 3 links are the final layer of your tiered link-building structure. These links point to your Tier 2 links and can be more diverse in terms of quality. Examples include:
- Blog Comments: Leave thoughtful comments on blogs with links to your Tier 2 content.
- Social Signals: Share your Tier 2 links on social media platforms to generate engagement and backlinks.
- Wiki Links: Add relevant links to your Tier 2 content on niche-specific wikis.
- Profile Links: Create profiles on directories or forums and link to your Tier 2 content.
SEO Considerations for Tier 3 Links:
- Focus on quantity over quality for Tier 3 links, but avoid spammy or irrelevant sources.
- Use nofollow links where appropriate to maintain a natural link profile.
- Monitor your backlink profile regularly to ensure no toxic links are harming your SEO efforts.
Best Practices for Tiered Link Building
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity: While Tier 2 and Tier 3 links can be lower in quality, your Tier 1 links must come from authoritative and relevant sources.
- Diversify Your Anchor Text: Use a mix of branded, generic, and keyword-rich anchor text to avoid over-optimization.
- Monitor Your Backlink Profile: Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to track your backlinks and identify any toxic links.
- Avoid Black-Hat Tactics: Steer clear of link farms, private blog networks (PBNs), or any manipulative practices that could lead to penalties.
- Create Link-Worthy Content: Invest in high-quality content that naturally attracts backlinks and serves as the foundation of your Tier 1 strategy.
Tools to Support Tiered Link Building
- Ahrefs: Analyze backlinks, track rankings, and find link-building opportunities.
- SEMrush: Conduct competitor analysis and identify potential link sources.
- Moz Link Explorer: Measure domain authority and track your backlink profile.
- BuzzStream: Streamline your outreach campaigns for Tier 1 link building.
- Hunter.io: Find email addresses for outreach purposes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-Optimizing Anchor Text: Using the same keyword-rich anchor text repeatedly can trigger search engine penalties.
- Ignoring Relevance: Building links from irrelevant websites can harm your SEO efforts.
- Neglecting Tier 1 Links: Focusing too much on Tier 2 and Tier 3 links without securing high-quality Tier 1 links can limit your success.
- Using Spammy Tactics: Avoid low-quality directories, link farms, or PBNs, as they can lead to penalties.
Conclusion
A well-executed tiered link-building structure can significantly enhance your website’s authority, visibility, and search engine rankings. By focusing on high-quality Tier 1 links and supporting them with Tier 2 and Tier 3 links, you create a robust backlink profile that mimics natural link-building patterns. Remember to prioritize quality, relevance, and diversity in your link-building efforts, and always adhere to SEO best practices to avoid penalties. With the right strategy and tools, tiered link building can become a cornerstone of your SEO success.
By implementing these techniques and continuously monitoring your backlink profile, you can stay ahead of the competition and achieve long-term SEO growth. However, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages carefully to ensure this strategy aligns with your overall SEO goals and resources.