Contents
- 1 What Is the UTC Time Zone? A Beginner’s Guide
- 1.1 What Does UTC Stand For?
- 1.2 The History of UTC
- 1.3 Why Is UTC Important?
- 1.4 How Is UTC Time Measured?
- 1.5 UTC vs GMT: What’s the Difference?
- 1.6 Is UTC a Time Zone?
- 1.7 UTC Offsets Explained
- 1.8 How to Convert UTC to Your Local Time
- 1.9 Tools That Use UTC Time Zone
- 1.10 Daylight Saving Time and UTC
- 1.11 Common Uses for UTC
- 1.12 Why Should You Care About UTC?
- 1.13 How to Set Your Devices to UTC
- 1.14 The Future of UTC
- 1.15 Final Thoughts
What Is the UTC Time Zone? A Beginner’s Guide
If you’ve ever looked at a digital clock, scheduled a Zoom meeting with someone in another country, or worked with international clients, you may have come across the term UTC. But what does it really mean? And why is it so important in our connected world? In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll break down what the UTC Time Zone is, why it matters, and how it impacts our daily lives.
What Does UTC Stand For?

UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time. It’s the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It’s not a time zone in the traditional sense but rather a baseline time reference used globally.
Unlike local time zones, which can change due to Daylight Saving Time (DST), UTC remains constant all year round. It’s the same in winter, summer, and everywhere in between.
The History of UTC
From GMT to UTC
Before UTC, we used GMT (Greenwich Mean Time). GMT was based on the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. While GMT is still used in some contexts, UTC has replaced it in most technical and scientific fields because it offers a more precise and stable reference.
UTC was officially adopted in 1960 and became the basis for civil timekeeping in 1972.
Why the Switch?
Unlike GMT, which is based on the Earth’s rotation (which isn’t perfectly stable), UTC combines atomic timekeeping with occasional adjustments called leap seconds to stay in sync with the Earth’s movement.
Why Is UTC Important?
The UTC Time Zone plays a crucial role in:
1. Global Communication
Whether it’s a video call, a news broadcast, or satellite data, synchronized time is essential for smooth communication.
2. Technology & Internet
Computer networks, databases, and servers rely on UTC to coordinate across different time zones. For example, file timestamps and log files often use UTC to avoid confusion.
All aviation operations use UTC to avoid errors. Pilots, air traffic controllers, and even GPS systems rely on it.
4. Scientific Research
In astronomy, space exploration, and global scientific collaboration, having a consistent time standard is critical.
How Is UTC Time Measured?
Atomic Clocks
UTC is based on time kept by atomic clocks, which are extremely accurate. These clocks measure the vibration of atoms (usually cesium or rubidium) to determine time intervals.
Leap Seconds
Because Earth’s rotation is not perfectly consistent, we occasionally add a leap second to UTC to keep it in sync with solar time. This happens about every few years.
UTC vs GMT: What’s the Difference?
Although people often use UTC and GMT interchangeably, they are technically different:
| Feature | UTC | GMT |
|---|---|---|
| Based on | Atomic time | Solar time |
| Used for | Global time standard | Time zones in UK & Commonwealth |
| DST changes | No | Yes (in UK) |
| Stability | Highly precise | Less stable |
GMT is a time zone, while UTC is a time standard.
Is UTC a Time Zone?
Technically, no. UTC is a time standard, not a geographical time zone. However, many time zones are defined as offsets from UTC, like:
- UTC+0: London (when not in DST)
- UTC+5: Pakistan Standard Time
- UTC-8: Pacific Standard Time (PST)
This makes UTC the foundation for every time zone in the world.
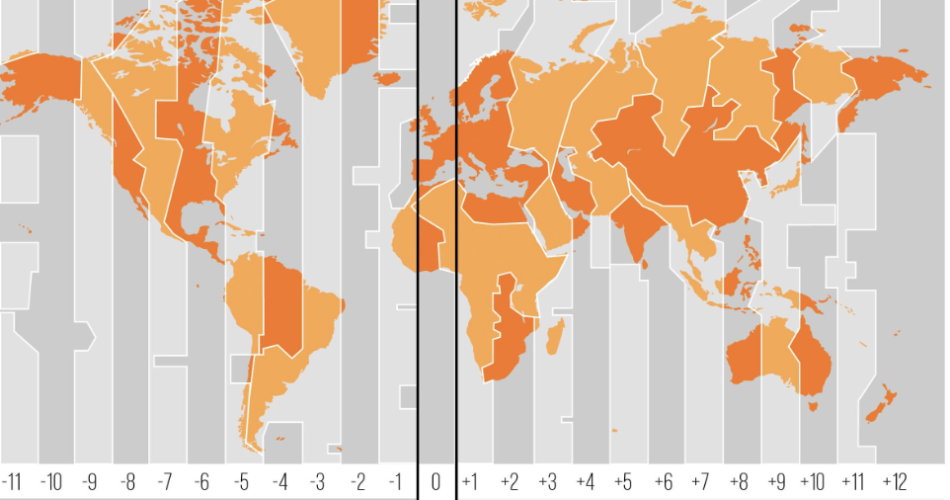
UTC Offsets Explained
Time zones across the globe are expressed as an offset from UTC. Here are a few examples:
| Time Zone | UTC Offset | Region |
| EST | UTC-5 | Eastern US & Canada |
| CET | UTC+1 | Central Europe |
| IST | UTC+5:30 | India |
| JST | UTC+9 | Japan |
| AEDT | UTC+11 | Eastern Australia (Daylight Time) |
Some countries use non-standard offsets like +5:30 or +9:45, adding more complexity to global coordination.
How to Convert UTC to Your Local Time
To convert UTC to your local time:
- Know your UTC offset. For example, if you live in New York and it’s winter, your time zone is UTC-5.
- Add or subtract the offset to get your local time.
Example: If it’s 15:00 UTC and you’re in New York (UTC-5), your local time is 10:00 AM.
You can also use online tools like timeanddate.com or your smartphone’s world clock.
Tools That Use UTC Time Zone
Many systems use UTC as a default to maintain consistency:
- Servers & Cloud Platforms (AWS, Google Cloud)
- Programming Languages (Python, JavaScript)
- Log Files (System logs, audit trails)
- Global Events (Launches, releases)
Using UTC helps eliminate confusion caused by daylight savings or varying local times.
Daylight Saving Time and UTC
One of UTC’s key benefits is that it doesn’t change for Daylight Saving Time (DST). Local times may shift, but UTC stays constant. This is why many global teams schedule meetings in UTC—everyone adjusts based on their local DST rules.
Common Uses for UTC
1. Global Business
Companies with international teams often schedule meetings in UTC to keep things simple.
2. Software Development
When coding applications, developers often log activities in UTC to avoid bugs caused by time zone issues.
3. Space Missions
NASA and other space agencies use UTC to coordinate launches, track satellites, and log mission data.
4. Weather Forecasting
Meteorologists use UTC to synchronize weather data across regions.
Why Should You Care About UTC?
Even if you don’t work in tech or science, understanding UTC can help you:
- Avoid scheduling errors across time zones
- Coordinate travel plans more effectively
- Interpret timestamps on websites, emails, and messages
- Use online services like remote work tools or trading platforms that run on UTC
How to Set Your Devices to UTC
Most operating systems let you switch to UTC time. Here’s how:
Windows
- Go to Settings > Time & Language
- Select Date & Time
- Change the time zone to (UTC)
macOS
- Open System Preferences
- Click Date & Time > Time Zone
- Uncheck “Set time zone automatically” and choose UTC
Smartphones
- Use World Clock or change the device’s default time zone in settings
The Future of UTC
There has been some debate about whether to eliminate leap seconds due to the complexity they add. Still, for now, UTC remains the gold standard for global timekeeping.
As technology evolves, the demand for consistent and accurate time will only grow—making UTC more important than ever.
Final Thoughts
The UTC Time Zone isn’t just a technical concept used by scientists and engineers. It’s a critical part of how our world stays in sync—from your smartphone to space stations. Whether you’re a frequent traveler, remote worker, or just curious, understanding UTC can help you navigate our increasingly interconnected world.
It’s stable, universal, and reliable—a true cornerstone of global communication and coordination. So the next time you see a meeting set for 14:00 UTC, you’ll know exactly what that means.
Meta Title: What Is the UTC Time Zone? A Beginner’s Guide to Coordinated Universal Time
Meta Description: Learn everything about the UTC Time Zone in this simple guide. Understand its purpose, how it works, and why it’s essential for global timekeeping.
FAQs About UTC Time Zone
What is the difference between UTC and Zulu time?
Zulu time is a military term that refers to the same time as UTC. The “Z” in Zulu time corresponds to the zero UTC offset. So, UTC and Zulu time are effectively the same.
Does UTC observe Daylight Saving Time?
No. UTC does not change with the seasons. This makes it a consistent time standard that avoids the confusion caused by local DST changes.
Can I set my phone to display time in UTC?
Yes. Most smartphones allow you to add UTC in the world clock feature, or set UTC as the default time zone in settings.
Why do tech companies use UTC?
Tech companies use UTC to ensure consistent and unambiguous timestamps across global systems. It helps prevent bugs and data sync issues.
Is UTC the same everywhere in the world?
Yes. One of UTC’s main advantages is its consistency. 12:00 UTC is the same whether you’re in New York, Tokyo, or London.