Imagine this: Your business is thriving, your team is productive, and your data is locked down tighter than a vault. But here’s the catch—cybercriminals are smarter, sneakier, and more relentless than ever. Traditional security models, which assume everything inside your network is safe, are like leaving your front door wide open. That’s where Zero Trust Reference Architecture comes in—a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity that operates on one simple rule: Never trust, always verify.
In today’s digital world, where threats can come from anywhere, Zero Trust Reference Architecture is the ultimate defense. It ensures no user, device, or application is trusted by default. Every access request is checked, double-checked, and monitored in real-time. It’s like having a high-security checkpoint for your digital assets, ensuring only the right people and devices get through.
Contents
What is Zero Trust Reference Architecture?

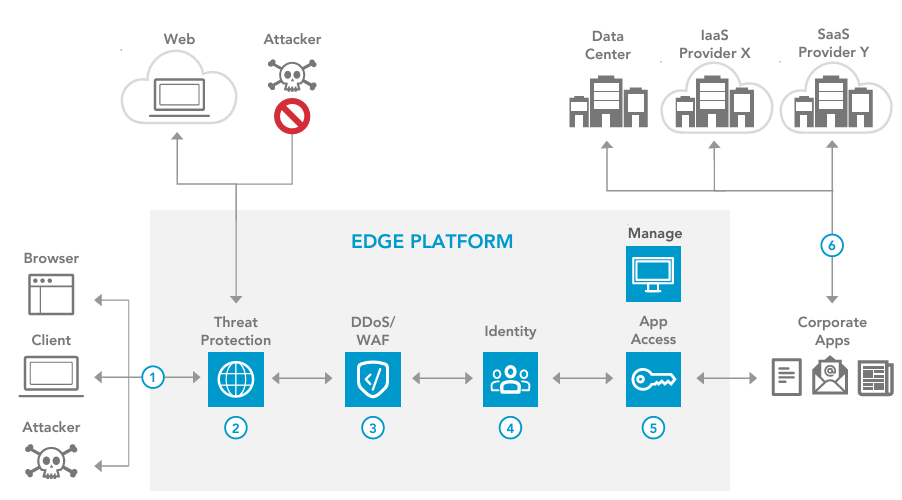
Zero Trust Reference Architecture is a framework for implementing the Zero Trust security model. The Zero Trust model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security, which focuses on defending the perimeter, Zero Trust assumes that threats can come from anywhere—inside or outside the network.
The Zero Trust Reference Architecture provides a blueprint for organizations to build a secure environment by:
- Verifying every user and device before granting access.
- Limiting access to only what’s necessary (least privilege access).
- Continuously monitoring and validating all activity.
This approach ensures that even if a hacker breaches your network, they can’t move freely or access critical resources.
Why is Zero Trust Reference Architecture Important?

- Protects Against Modern Threats: With remote work, cloud computing, and IoT devices, the traditional network perimeter has disappeared. Zero Trust secures your data no matter where it is.
- Reduces Risk: By verifying every access request, Zero Trust minimizes the risk of data breaches and insider threats.
- Improves Compliance: Many industries require strict data protection measures. Zero Trust helps you meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and more.
- Enhances Visibility: Zero Trust provides real-time monitoring, giving you a clear view of all activity across your network.
- Future-Proofs Your Security: As technology evolves, Zero Trust adapts to new threats and challenges.
Key Components of Zero Trust Reference Architecture
To implement Zero Trust effectively, your architecture should include these core components:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that only authorized users and devices can access your resources. This includes:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) to enforce least privilege access.
2. Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation divides your network into smaller, isolated zones. This limits the spread of threats and ensures that users only access the resources they need.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Analytics
Zero Trust requires constant monitoring of user behavior, device health, and network activity. Advanced analytics and AI can detect anomalies and respond to threats in real-time.
4. Endpoint Security
Every device connected to your network must be secure. Endpoint security solutions ensure that devices comply with security policies and are free from malware.
5. Encryption
Encrypting data at rest and in transit ensures that even if it’s intercepted, it can’t be read by unauthorized parties.
6. Policy Enforcement
Zero Trust relies on strict policies to control access. These policies should be dynamic, adapting to changes in user behavior, device status, and threat levels.
How to Implement Zero Trust Reference Architecture
Implementing Zero Trust Reference Architecture may seem daunting, but it can be broken down into manageable steps:
1. Assess Your Current Environment
Start by mapping out your network, identifying all users, devices, and applications. Understand where your sensitive data resides and how it’s accessed.
2. Define Your Policies
Create clear access policies based on the principle of least privilege. Determine who needs access to what and under what conditions.
3. Deploy IAM Solutions
Implement multi-factor authentication and role-based access control to verify users and limit access.
4. Segment Your Network
Use micro-segmentation to divide your network into secure zones. This prevents lateral movement by attackers.
5. Monitor and Analyze
Deploy tools for continuous monitoring and analytics. Look for solutions that use AI to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
6. Educate Your Team
Ensure that employees understand the importance of Zero Trust and follow security best practices.
7. Iterate and Improve
Zero Trust is not a one-time project. Regularly review and update your policies, tools, and processes to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Benefits of Zero Trust Reference Architecture
- Stronger Security: Protects against both external and internal threats.
- Better Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements and avoid costly fines.
- Improved Efficiency: Automates security processes, reducing the burden on IT teams.
- Greater Flexibility: Supports remote work, cloud computing, and other modern business needs.
Challenges of Zero Trust
While Zero Trust offers many benefits, it’s not without challenges:
- Complexity: Implementing Zero Trust requires careful planning and coordination.
- Cost: Upgrading your security infrastructure can be expensive.
- User Resistance: Employees may find new security measures inconvenient.
However, the long-term benefits far outweigh these challenges.
Final Thoughts
In a world where cyber threats are constantly evolving, Zero Trust Reference Architecture provides a robust and future-proof solution. By adopting this approach, you can protect your business, comply with regulations, and stay ahead of attackers.