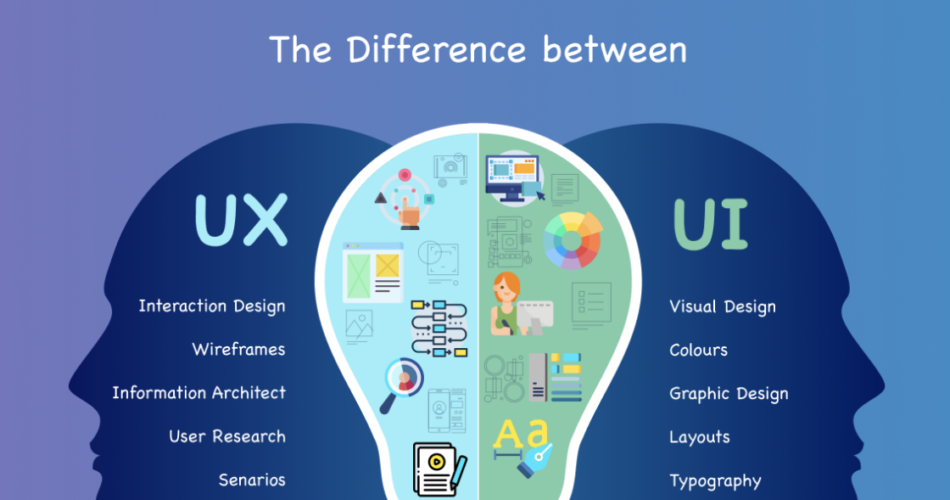
User experience (UX) design and user interface (UI) design are pivotal in crafting exceptional digital experiences. UX design focuses on boosting user satisfaction by enhancing usability, accessibility, and pleasure derived from interacting with a product or service. On the flip side, UI design zeroes in on the visual and interactive elements that users engage with. Together, these disciplines form the core of what is UX/UI design, effectively clarifying the UI vs UX design debate and deepening the understanding of the UI/UX meaning.
The Importance of User Experience
In today’s competitive digital landscape, the significance of user experience (UX) design is unparalleled. A stellar UX can significantly amplify user engagement, elevate conversion rates, and ultimately, boost customer satisfaction. Conversely, a subpar user experience might lead to user frustration, elevated bounce rates, and a tarnished brand image. Hence, investing in UX design is crucial for businesses aiming to excel and flourish in the digital era.
The Role of UI Design in User Experience
While UX design zeroes in on the overarching user experience, UI design is crucial in dictating how users interact with a product or service. UI design includes visual components like layout, typography, color schemes, and interactive elements such as buttons and icons. By crafting visually attractive and intuitive interfaces, UI design plays a significant role in enhancing the overall user experience, facilitating users in achieving their objectives and navigating through the digital product seamlessly.
Principles of UX/UI Design
To forge exceptional user experiences, designers must adhere to specific UX/UI design principles. These guidelines serve as the foundation for creating user-centric digital products that resonate with audiences, ensuring that both UX and UI designers work in harmony to achieve the best outcomes.
- SimplicityKeeping the design simple and intuitive is paramount. This approach enables users to swiftly grasp how to navigate and interact with the product, steering clear of clutter and unnecessary complexity. It’s a fundamental principle that UX and UI designers both prioritize to ensure a seamless user experience.
- ConsistencyEmploying consistent design elements, such as color schemes, typography, and navigation patterns, fosters a sense of familiarity and enhances the user experience by making it more cohesive. This consistency is a key aspect of UX design, helping to create a predictable and comfortable environment for users.
- HierarchyEstablishing a clear hierarchy of information is essential. It aids users in prioritizing and comprehending the content more effectively. Designers can guide users’ attention through visual cues like size, color, and placement, an approach deeply rooted in the principles of UX design and information architecture.
- FeedbackProviding immediate feedback to user actions is crucial for helping them understand the impact of their interactions. This can be achieved through visual cues, animations, or notifications, embodying the essence of interaction design. It’s a practice that enhances the user experience by making interactions feel more engaging and responsive.
- AccessibilityDesigning with accessibility in mind is vital to ensure that all users, including those with disabilities, can access and interact with the product. Factors such as color contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility are key considerations, underscoring the importance of inclusive UX design practices.
User Research and User Testing

Prior to embarking on the design journey, conducting user research and testing is imperative. User research enables UX designers to unearth insights into user behaviors, needs, and preferences, which are invaluable for crafting a user-centered design that appeals to the target audience. User testing, including methods like A/B testing, allows for observing users interacting with prototypes or existing products to pinpoint usability issues and collect feedback for enhancements.
Creating Wireframes and Prototypes
Wireframes and prototypes, integral to the UX and UI design process, serve as the foundational blueprint for the final design. These low-fidelity representations, often referred to as website wireframes, outline the digital product’s structure and layout, focusing on the placement of elements and overall flow. Prototypes, offering a more interactive experience, allow users to engage with the design and offer feedback. Both wireframes and prototypes are crucial in the iterative design process, aiding UX designers in refining and enhancing their designs through valuable user feedback.
The Elements of Effective UI Design
Effective UI design involves several key elements that contribute to a seamless user experience:
- LayoutA well-structured layout, pivotal in UX design, ensures that information is organized logically and is easy to navigate. Employing grid systems and visual hierarchy significantly contributes to creating an effective and user-friendly layout, underpinning the principles of information architecture in UX and UI design. This approach facilitates a seamless user experience, guiding users through the content effortlessly.
- TypographyChoosing the right fonts and typography is essential in enhancing readability and communicating the brand’s personality, key aspects of UX, UI, and graphic design. Factors such as font size, line spacing, and font pairing are crucial considerations in creating an engaging user interface that captivates users and ensures the text is accessible.
- ColorColors, a core component of UX, UI, and visual design, evoke emotions and can significantly influence user behavior. A deep understanding of color theory and selecting appropriate color schemes are vital in creating visually appealing and cohesive designs that resonate with users. This knowledge enables designers to craft experiences that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also emotionally engaging.
- VisualsHigh-quality images, icons, and illustrations play a significant role in UX design, enhancing the user experience and effectively communicating information. Visuals should be purposefully used to support the content and not overwhelm the design, adhering to the principles of UX and UI design to create an engaging user interface that captures users’ attention and aids in navigation.
- MicrointeractionsMicrointeractions, small but impactful elements of interaction design, are subtle animations or responses that occur in response to user actions. They provide feedback and significantly enhance the overall user experience, embodying the essence of interactive design in UX and UI. These details contribute to a more intuitive and engaging digital environment.
Color Theory and Typography in UX/UI Design
Color theory and typography are significant in UX, UI, and visual design, enhancing the user experience. Color choices, influenced by color psychology, can evoke specific emotions and influence user behavior, while the right typography enhances readability, hierarchy, and overall aesthetics, effectively communicating the brand’s personality. Together, they form a powerful duo that shapes user perceptions and interactions.
Responsive Design and Mobile Optimization
With the ubiquity of smartphones and tablets, designing for mobile devices has become essential in UX and product design. Responsive design ensures that websites or applications adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices, offering an optimal user experience across all platforms. This adaptability is crucial in meeting the diverse needs of today’s mobile-first audience.
Usability Testing and Iterative Design
Usability testing, a cornerstone of the UX design process, allows designers to observe user interactions, identify usability issues, and gather feedback for iterative improvements. This process ensures that the final product aligns with the needs and expectations of the target audience, embodying the principles of UX design. Through usability testing, UX designers can refine their designs to enhance user satisfaction and engagement.
Tools and Software for UX/UI Design
The UX/UI design process is supported by a wide range of tools and software, from wireframing and prototyping tools like Sketch and Adobe XD to collaboration and project management platforms such as InVision and Trello. These tools, along with usability testing tools, analytics platforms, and design asset libraries, further enhance the design process, offering valuable insights to UX and UI designers. They streamline workflows and facilitate collaboration, making it easier to bring creative visions to life.
The Future of UX/UI Design
As technology continues to evolve, the realms of UX design and UI design are also advancing. Emerging trends like voice user interfaces, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence are opening up thrilling opportunities for UX and UI professionals to craft even more immersive and intuitive user experiences. Keeping pace with the latest trends, technologies, and user expectations is essential for those in the UX/UI field to stay ahead, merging the foundational principles of UX and UI design with cutting-edge product design effortlessly.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of UX/UI design is a continuous journey that demands a profound comprehension of user behaviors, preferences, and expectations. By dedicating themselves to crafting exceptional user experiences, adhering to design principles, conducting thorough user research and testing, and leveraging the appropriate tools and software, UX/UI designers are equipped to create digital products that captivate and engage users. With the technological landscape constantly evolving, the future of UX/UI design is ripe with possibilities for even more intuitive and immersive user experiences. Thus, embracing the art of UX/UI design means unlocking the potential to create outstanding digital experiences through a harmonious blend of UX and UI design skills, along with a deep understanding of user interface design.