Typography and font are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct aspects of design and communication. Understanding the difference between typography and font is crucial for anyone involved in graphic design, web development, or any field that involves visual communication. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of typography and font, exploring their definitions, significance, and how they work together to create effective design.
Typography vs. Font
Typography:
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type, which includes letters, numbers, symbols, and other characters, to make written language legible and visually appealing. It encompasses a wide range of elements, including:
Typefaces:
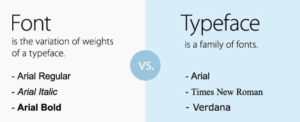
Typefaces are sets of characters that share a similar design style. They include various styles like serif, sans-serif, script, and decorative fonts. Popular typefaces include Times New Roman, Helvetica, and Comic Sans.
Typeface Families:
Each typeface often includes various weights (e.g., regular, bold, italic) and variations that maintain a consistent design style. These variations provide designers with flexibility in creating hierarchy and emphasis within text.
Kerning:
Kerning refers to adjusting the space between individual characters to ensure balanced and harmonious text. Proper kerning improves readability and aesthetics.
Line Spacing:
Line spacing, also known as leading, determines the vertical space between lines of text. Proper line spacing contributes to readability and overall text cohesion.
Tracking:
Tracking involves adjusting the spacing between all characters in a block of text. It can affect the readability and visual appeal of a text block.
Font:
A font, on the other hand, is a specific instance or variation of a typeface. It is a digital file that contains all the characters, symbols, and glyphs associated with a particular typeface. Fonts come in different file formats (e.g., .ttf, .otf) and can be installed on a computer or used in design software. When you choose a font, you are selecting a specific style and weight within a typeface family. For example, Arial Bold 12pt is a font, while Arial is the typeface.
Key differences between typography and font:
- Typography is a broader concept encompassing the art and science of arranging type, including considerations of layout, hierarchy, and visual appeal.
- Fonts are specific digital files representing a typeface. They are the practical tools used to implement typography in design.
- Typography involves decisions about typefaces, typeface families, kerning, line spacing, tracking, and layout, while fonts are the tangible assets used to execute these decisions.
- Typography is about the creative and strategic use of fonts to convey a message effectively, while fonts themselves are the building blocks for typographic designs.
Conclusion:
In the realm of design and communication, understanding the distinction between typography and font is essential for creating visually compelling and readable content. Typography encompasses a wide range of design principles and techniques, while fonts are the practical tools that make typography come to life. By mastering both typography and fonts, designers and communicators can enhance the impact and effectiveness of their visual messages, ensuring that content is not only beautiful but also legible and communicative.

